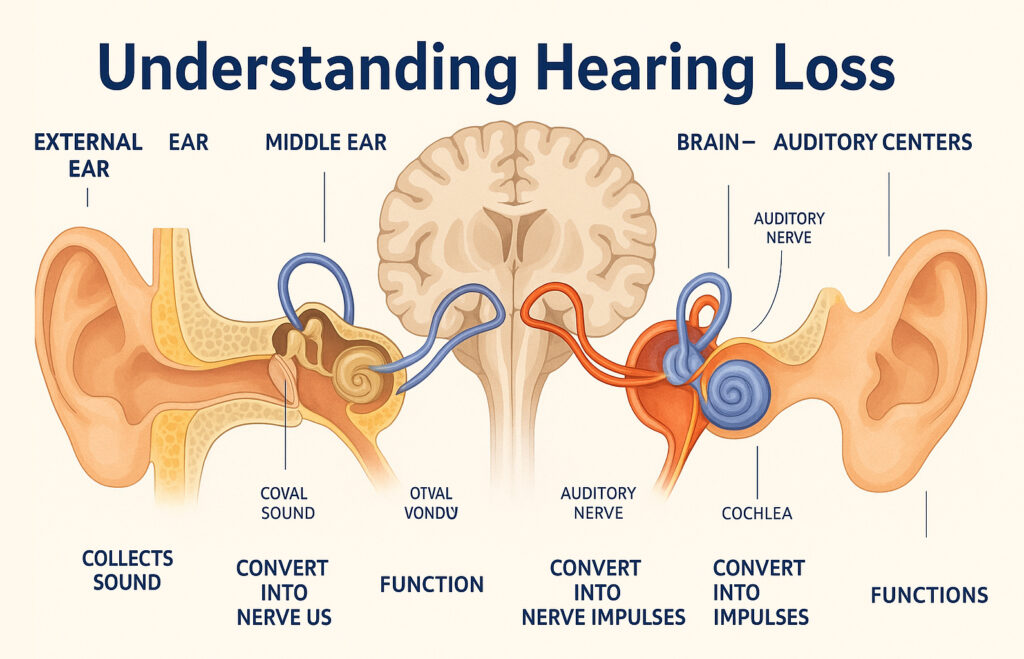
Introduction
Understanding hearing loss requires knowledge which depends on your age point and encompasses symptom recognition and cause determination and therapeutic considerations. Millions of people suffer from hearing loss which develops at any point in life. Early diagnosis makes a difference in treatment outcomes and quality of life.” This guide explains the types of hearing problems, common conditions that compromise hearing and how to improve your hearing health.
What is Hearing Loss?
The failure to hear with diligence equals hearing loss (or hearing impairment) just like the inability to hear like a person with typical hearing ability. The condition develops due to aging processes and physical trauma as well as without identifiable medical causes. A person might experience hearing loss to a varying degree from mild to profound and either completely or partially. People understanding hearing loss can decide well between treatment options together with lifestyle modifications.
How to Understanding Hearing Loss?
Different medical conditions exist as causes of hearing deficiency. Common examples include:
1. Ear Infections
Ear infections that become persistent over time will harm the inner ear structures which results in lasting hearing impairment. By understanding infection-related hearing loss patients can seek early symptom management while stopping permanent hearing damage from happening.
Types of Ear Infections
There exist two fundamental groupings of ear infections namely acute and chronic infections. Alongside quick recovery with treatment acute infections vanish but persistent infections lead to permanent harm to the ear structures.
Symptoms of Ear Infections
Ear infections commonly display three main symptoms which are painful sensations combined with discharge from the ears and a temporary period of hearing loss. The symptoms become worse when left untreated because they lead to permanent hearing damage.
Preventing Ear Infections
Effective ear hygiene measures supplemented by early medical help prevent ear infections from resulting in lasting hearing impairment. Suitable ear cleaning procedures combined with minimal exposure to moisture help decrease infection occurrence.
Acute vs. Chronic Infections
Short-term acute infections respond well to medication yet chronic infections develop permanent damage to hearing structures if physicians do not provide proper treatment.
2. Meniere’s Disease
The inner ear fluid buildup causes Meniere’s Disease to generate vertigo alongside hearing problems. Unpredictable symptoms appear because the condition interferes with both balance and hearing ability.
Causes of Meniere’s Disease
Inner ear fluid buildup creates disorders in balance structures which then cause both vertigo along with hearing reduction.
Symptoms of Meniere’s Disease
The signs of Meniere’s disease involve brief periods of vertigo together with tinnitus and worsening hearing. Azure symptoms occur either as short-term encounters or they evolve progressively worse throughout time.
Treatment Options
Medical experts manage Meniere’s disease symptoms through various treatments although this disorder has no available cure. Medical treatments alongside eating modifications as well as surgical interventions serve to minimize Meniere’s disease manifestations.
Dizziness, Tinnitus, and Hearing Loss
Patients with Meniere’s disease show three primary symptoms consisting of vertigo situations along with tinnitus noises and hearing losses. Symptoms of Meniere’s disease appear in different levels of intensity while their duration remains different for each person.
3. Otosclerosis
The abnormal bone growth affecting middle ear structures during otosclerosis blocks proper sound transmission which causes hearing loss. Otosclerosis mostly develops within the stapes bone which serves as one of the three tiny bones located within the middle ear.
What is Otosclerosis?
The stapes bone fails to vibrate correctly because abnormal bone growth occurs during otosclerosis. Sound transmission stops efficiently reaching the inner ear because of this condition leading to hearing limitations.
Symptoms of Otosclerosis
The leading symptom of this condition involves slow hearing deterioration and tinnitus develops simultaneously. Hearing loss gradually progresses into a more severe degree over time.
Treatment for Otosclerosis
The available treatments for otosclerosis involve wearing hearing aids to boost sound amplification and surgical procedures to fix or replace defective stapes bones for better hearing abilities.
gradual Hearing Loss and Tinnitus
Tinnitus along with gradual hearing loss occurs as a symptom of otosclerosis. Otosclerosis degenerates to worse levels when medical treatment is absent.
4. Diabetes and Hearing Loss
The bloodstream among all body parts including the internal structures of the ear becomes affected by diabetic conditions. The diagnosis and treatment of hearing loss requires sufficient understanding for diabetic patients.
How Diabetes Affects Hearing
Hearing loss happens when diabetes impairs blood circulation which reduces necessary bloodstream and nutritional delivery to the inner ear. Denial of hearing occurs due to diabetic sensorineural hearing loss.
Symptoms of Hearing Loss in Diabetics
Diabetic patients might notice the first indications of hearing loss through their inability to understand speech particularly when in noisy situations. People require routine hearing assessments because such testing helps detect hearing issues in their early stages.
Managing Diabetes Related Hearing Loss
Effective blood sugar control helps stop hearing loss development and slows its progression. Hearing health monitoring happens through stretch tests combined with expert audiologist evaluations.
Early Warning Signs to Look For
The early warning indications of diabetes-induced hearing loss consist of struggling to hear high-pitched sounds and having trouble understanding conversations within noisy settings. Routine testing of hearing will help identify health issues at their onset.
People understanding hearing loss origins can implement active steps to control their hearing health. Early intervention becomes critical for preserving good hearing function because of its role in combination with medical treatment and ear hygiene along with lifestyle modifications.
Understanding Hearing Loss and Its Types
1. Conductive Hearing Loss
Due to blockages or damage to the outer or middle ear, like earwax buildup or a perforated eardrum. Helpful resources exist regarding the sources of Conductive Hearing Loss and its possible treatment options.
2. Sensorineural Hearing Loss
Harvard Health PublicationsWhen the inner ear or auditory nerve is damaged, usually from aging, noise or genetics. The medical origins of Sensorineural Hearing Loss and its possible treatment solutions.
3. Mixed Hearing Loss
Both the outer/middle ear and inner ear involved — sensorineural and conductive loss. Visit here to learn about Mixed Hearing Loss and how it affects.
Testing Sooner: The Early Warning Signs of Hearing Loss in Adults
Recognising early signs is crucial for prevention and treatment. Look out for:
- Listening to conversations becomes challenging when background noises are elevated in public settings
- Repeating people frequently
- Getting devices to crank the volume up
- Not sure if other people are mumbling
- Tinnitus (ringing in your ears)
Hearing loss: What to know
The starting point for understanding hearing loss management consists of understanding its nature. You should seek a professional audiologist directly after symptoms appear which include following conversations poorly or experiencing ringing in the ears or needing to turn up the volume too often.
The available clinical tests enable experts to determine listening loss progression so they can decide appropriate therapeutic interventions. Early diagnosis of hearing impairment shields it from additional deterioration.
The 4 Stages of Hearing Loss
Mild — Difficulty hearing soft-sounding things, or speech in noisy environments
Moderate — Trouble following conversations, even in quiet situations.
Severe – Cannot hear loud noises
Profound – Almost or totally unable to hear, usually needing cochlear implants
Natural Methods of Reversing Hearing Loss
Age-related or genetic hearing loss is typically irreversible, but some preventive steps may help:
- Regular hearing check-ups
- Using hearing protection and avoiding loud noises
- Eating right and working out to help the ears stay healthy
- New Treatments for Hearing Loss
Due to advances in technology, treatment options have improved significantly:
Hearing Aids – These are used to amplify sound and assist in communication
Cochlear Implants – for severe hearing loss; bypasses damaged ear parts
Bone Anchored Hearing Aids (BAHA) – Best for ear deformities
The 4 Types of Hearing Loss
Part of understanding hearing loss is knowing its major types:
Sensorineural Hearing Loss – Permanent damage of both the cochlea and auditory nerve exists.
Conductive Hearing Loss – The entry of sound is blocked by any issues within the outer or middle ear sections.
Mixed Hearing Loss – A combination of the above two types
Auditory Processing Disorder (APD) – Difficulty in the brain correctly interpreting sounds
Conclusion:
Your ability to address hearing impairment flourishes with proper understanding hearing loss. Delayed help seeking must be ignored whenever someone you know or yourself present signs of hearing difficulties. The early use of hearing aids coupled with testing brings substantial advantages for your daily life quality.
Think you have hearing loss? Take our free hearing test: 01711-636214
FAQs:
1. The 4 P’s of Hearing Loss: What Are They?
Presbycusis — Age-related hearing loss
It is not surprising that limited access to hearing care is an important part of the issue facing the deaf or hearing-impaired community when involved in dealing with the disability.
Psychosocial Impact- Effect on psychological and social well-being
Physical Health – Chronic illnesses e.g., diabetes, hypertension
2. What Are the Five Levels of Hearing?
Normal – 0–20 decibels
Mild – 21–40 decibels
Moderate – 41–60 decibels
Severe – 61–80 decibels
Profound – Over 80 decibels
3. How can you know for sure that there is hearing loss?
You should have your hearing evaluated by an audiologist who will perform tests for correct diagnosis. What it actually tests is your sensitivity to different sound frequencies and intensities.
4. How to Prevent Hearing Loss?
23 Avoid loud surroundings or wear ear protection
Testing hearing regularly, particularly for people with risks
Practice good ear hygiene — do not insert objects into the ear
Eat well — a healthy diet and exercise help with circulation
